Java容器源码阅读记录
前言
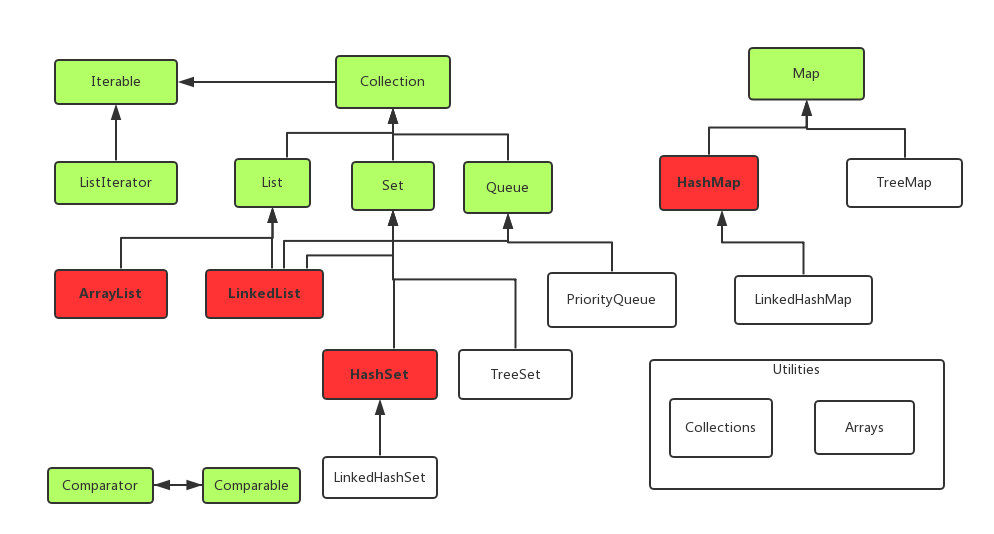
首先还是要放出这张大图,想要详细理解容器源码,他们之间的继承实现关系必须了熟于心。
ArrayList相关
ArrayList初始化
1 | /** |
这里的EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA值为0,初始化ArrayList时默认长度为零,不拥有默认大小
ArrayList的扩容
1 | /** |
ensureCapacity方法可由开发者调用,当调整的容量低于DEFAULT_CAPACITY时,只要有容量扩大需求,都会至少保证DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10的大小。
1 | /** |
实际扩容时调用的是grow()方法,可以看到,ArrayList在有扩容需求时会将原来的数组中的元素使用Arrays.copyOf方法复制到一个新的数组中,并且每次容量的增长为原来容量的1.5倍。
因此在使用ArrayList时,因为扩容代价较高,应尽量指定容量
ArrayList中的modCount
modCount变量用于记录该ArrayList的变更次数,包括add,remove,addAll,removeRange,clear方法,每操作一次这些方法,modCount的值就++。
modCount继承自AbstractList,该类中有iterator()方法使用了一个私有内部成员类Itr,Itr中有一个属性expectedModCount,在初始化的时候expectedModCount = modCount。
在对一个集合对象进行迭代操作时,如果不限制集合元素的操作,那么一些add或者remove操作可能会引起迭代错误,因此在AbstractList中使用了判断modCount和expectedModCount是否相等来规避这些风险。
HashMap相关
HashMap容量
1 | public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor){ |
HashMap的构造函数,参数一是桶容量大小,参数二是扩容阈值,默认0.75,即使只传桶容量,也会调用上述构造方法,loadFactor=0.75。还有一个变量叫threshold,threshold = loadFactor * capacity,就是扩容的阈值,当达到这个容量的时候就需要出发扩容机制,0.75时可以理解为装满四分之三就触发扩容。
HashMap的初始化在不指定容量大小的时候是16,并且保证初始化时容量大小总是2的n次方大小,根据HashCode查找数组位置的方法如下:
1 | /** |
length设置成2的n次方是有意义的,比如这里和HashCode的“与”运算,和2的n次方-1这样的全1二进制做与,可以保证数组的每个位置的index都有,比如1110,那么HashMap的数组1位置就永远不可能有值能放过来,因为没有数能和1110做“与”结果为1。()
HashMap的扩容
1 | /** |
因为HashMap的容量设置成2的n次方有利于提高利用率,所以当map中包含的Entry的数量大于等于threshold,触发扩容时扩大的容量倍数也是2倍。
HashSet
HashSet底层使用HashMap实现,构造方法上使用HashMap基本也是使用HashMap的,主要的区别在于HashMap存储键值对,HashSet仅仅存储对象,因为HashMap中的key是惟一的,所以这个特性被HashSet使用来保证存储对象的唯一性。
1 | /** |
在往HashSet里插入元素时,调用HashMap的put方法,如果该元素已经存在就返回false,不存在就返回true。
在我们日常使用HashSet时,要注意自己重写hashCode()和equal()方法,这样才能确保自己的比较的正确性。
HashTable
HashTable基本可以等价于HashMap,大体上只有这些区别:
HashTable是线程安全的,多个线程可以共享一个HashTable,HashMap不是synchronized的,但是ConcurrentHashMap是HashTable的一种替代,并且扩展性比HashTable更好。
HashMap的迭代器是Iterator,是fail-fast迭代器,当有其他线程改变HashMap的结构时就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException,而HashTable使用的是enumerator迭代器,不是fail-fast的。
单线程环境下,HashMap的性能比HashTable好。
LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap的有序性
LinkedHashMap和HashMao的主要区别在于前者的Entry是用一个双向链表维护的,这个链接列表定义了迭代的顺序,并且该迭代顺序是由插入顺序或者访问顺序决定的。
1 | /** |
LinkedHashMap中的accessOrder()来决定迭代顺序,为true则按访问顺序排序,越近访问的位置越靠后,false为按照插入顺序,最近插入的位置越靠后。
基本的初始化等操作全部与HashMap原理一致,只是多了recordAccess方法,在每次操作时重新排序,将最近操作的Entry放到最后。因为链表的移位操作,增加、删除操作都是常量级别的消耗,所以不会带来性能的损失。
LinkedHashMap与LRU缓存
LRU - Last Recent Use,由于LinkedHashMap能存储最近访问的功能,我们可以使用它来设计缓存,LinkedHashMap本身已经把最常读取的放在链表的最后。
在实现一个简单的LRU缓存功能时,我们只需要设置一个阈值,重写LinkedHashMap的removeEldestEntry方法,去除那些很久没有访问的Entry就行。
LinkedHashSet
继承自HashSet,基于LinkedHashMap,存的内容只有值,并且也维护着一个运行所有条目的双重链接列表。
LinkedList
基于链表实现,和ArrayList的主要区别就在于访问的性能,LinkedList的插入删除操作更好,但是随即访问操作要比ArrayList差。
其他
transient关键字
看源码过程中看到了很多transient关键字,简单了解了一下:
Java中的序列化和反序列化:
- 序列化:将一个对象转换成一串二进制表示的字节数组,通过保存或转移这些自己数据来达到持久化的目的,例如写到文件中等。
- 反序列化:将字节数组重新构造成对象。
java的transient关键字在序列化过程中为我们提供了便利,对需要通过序列化实现持久化的对象,首先实现Serilizable接口,将不需要序列化的属性前添加关键字transient,序列化对象的时候,这个属性就不会序列化到指定的目的地中。
这样HashMap等容器在序列化的时候,其容量大小,扩容阈值等这些容器内部变量就不会被序列化存储。